The Global Risks Report: Uncovering the Startling Threats That Matter Most 2022
The Global Risks Report: Uncovering the Startling Threats That Matter Most 2022
We are now in a world where threats are not just the stuff of personal or community concerns, but loom large on national and international stages. Many of you will be aware that there are institutions already tackling these colossal issues? Among them, the World Economic Forum (WEF) has recently unveiled its 2022 Global Risks Report, an intriguing document that lays bare the most pressing dangers our world faces. Brace yourself as we delve into the report's most concerning findings.
A Glimpse of the Global Outlook: Hold on to your hats, because the global outlook is far from rosy. According to the report, over 90% of survey respondents foresee a negative trajectory for the world.
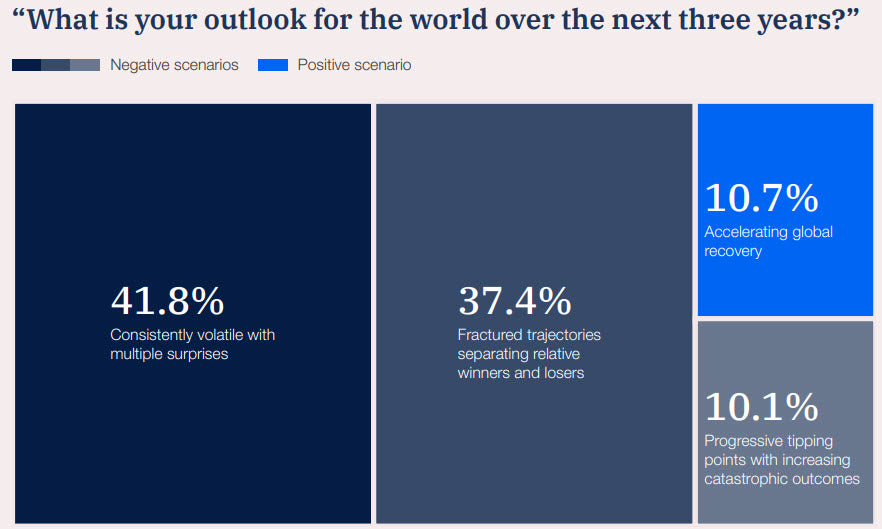
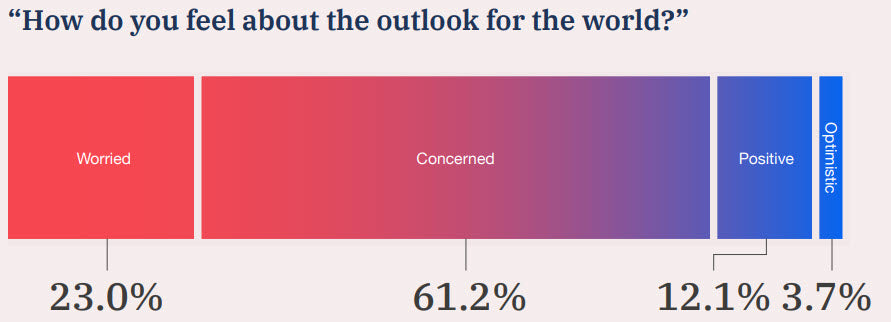
But what are the underlying reasons for this pessimistic outlook? Let's explore the top ten medium-term risks that have experts on edge:
-
Climate action failure: Climate action failure refers to the inability of societies, governments, and industries to effectively address and mitigate climate change. This includes not meeting emission reduction targets, failing to adopt sustainable practices, and neglecting to invest in clean energy technologies. The consequences of climate action failure are far-reaching and include rising global temperatures, increased frequency and severity of natural disasters, and disruptions to ecosystems and food supplies.
-
Extreme weather: Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes, floods, heatwaves, and droughts, are becoming more frequent and severe as a result of climate change. These events can lead to loss of life, property damage, economic disruption, and increased pressure on emergency services and infrastructure. Additionally, extreme weather can exacerbate other risks, such as food and water shortages, as well as contribute to the spread of infectious diseases.
-
Biodiversity loss: Biodiversity loss refers to the decline or disappearance of plant and animal species due to factors such as habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change. Losing biodiversity can have cascading effects on ecosystems and lead to a reduction in essential services they provide, such as pollination, water purification, and climate regulation. This, in turn, can affect human well-being, food security, and economic stability.
-
Social cohesion erosion: Social cohesion erosion is the weakening of social bonds and connections within societies, leading to increased tensions, divisions, and conflicts. This can be fuelled by factors like income inequality, political polarization, discrimination, and rapid cultural or demographic changes. As social cohesion erodes, trust in institutions and community resilience may decline, making it difficult for societies to effectively respond to and recover from crises.
-
Livelihood crisis: A livelihood crisis occurs when individuals or communities face significant disruptions to their income sources, employment opportunities, or access to essential resources, such as food, water, and healthcare. This can result from economic downturns, natural disasters, conflicts, or other destabilizing events. Livelihood crises can lead to poverty, malnutrition, displacement, and social unrest.
-
Infectious diseases: Infectious diseases pose a significant threat to public health and can spread rapidly, particularly in our increasingly interconnected world. Outbreaks and pandemics can strain healthcare systems, disrupt economies, and contribute to social unrest. Factors such as climate change, urbanization, and deforestation can also increase the likelihood of new infectious diseases emerging or existing ones re-emerging.
-
Human environmental damage: Human activities, such as deforestation, pollution, and overfishing, can cause significant and often irreversible harm to the environment. This damage can lead to the loss of vital ecosystems, the depletion of natural resources, and increased vulnerability to natural disasters. Ultimately, human environmental damage threatens the well-being of both current and future generations.
-
Natural resource crisis: A natural resource crisis occurs when essential resources, such as water, arable land, and minerals, become scarce due to overconsumption, depletion, or degradation. This can lead to increased competition, price volatility, and potential conflicts over access to these resources. Furthermore, a natural resource crisis can have significant impacts on food security, economic stability, and environmental quality.
-
Debt crises: Debt crises arise when governments, corporations, or individuals are unable to repay their debts or borrow further to meet their obligations. This can lead to financial instability, economic recessions, or even collapse. Debt crises can be triggered by factors such as unsustainable borrowing, economic shocks, or policy mismanagement. The consequences of a debt crisis can include austerity measures, job losses, and social unrest.
-
Geopolitical confrontation: Geopolitical confrontation refers to conflicts or tensions between nations or groups that arise from competing interests, territorial disputes, or ideological differences. Such confrontations can manifest as trade wars, cyberattacks, military standoffs, or even full-scale armed conflicts. Geopolitical confrontations can disrupt global stability, trade, and cooperation, leading to economic uncertainty and increased risks for all nations involved. In extreme cases, these confrontations can escalate into large-scale wars with devastating consequences for human lives, infrastructure, and the environment.
Please note: This report was published before the Russian invasion, which has since spawned new global threats.
The Domino Effect: As if plucked straight from a sci-fi thriller, these risks are already playing out in real time. From monkeypox and skyrocketing food prices to the Russia-Ukraine war, water shortages, and soaring energy costs, the world is feeling the tremors of these challenges. To top it off, a palpable sense of societal fragmentation hangs in the air.
The Food Factor: A common thread that weaves through many of these risks is their impact on food production capabilities (climate change, natural resource availability, environmental damage) and food prices (livelihood crises, debt crises). The consequences of these threats cannot be overstated.
In Good Company: If you're an ordinary citizen feeling uneasy about the near future of our society and its way of life, rest assured you're in good company. Your concerns are echoed by a significant proportion of experts and leaders worldwide, united in their mission to confront these daunting challenges head-on.
To become a little more prepared to face these potential threats, you can visit our Emergency Food guide, or follow the link to find out how to create a Household Food Security Plan.
We have also carried an assessment of myriad of risks facing UK society, which can be viewed here: Current Risks & Challenges facing UK society - our Top 50.
Suggested Articles
Is the world becoming a more dangerous place?
We were interested in building an understanding of whether the UK population consider the world to be becoming more d...
Mainstream news versus YouTube & Social Media
There is a sense that society has become increasingly divided in recent years. Whether it is traditional class divide...
Pandemic Implications
The sustained Covid-19 pandemic, described by some as a ‘black swan event’ has impacted the world in a huge number of...




